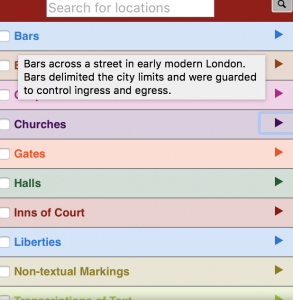
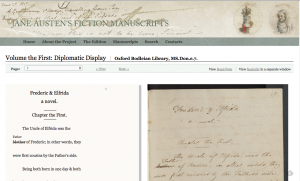
Often times when historians are analyzing an archive, specifically one that is large in size and may take a long time to analyze fully, they run into some trouble with a term that Micki Kaufman uses in her project Quantifying Kissinger; “information overload.” This over abundance of information usually requires multiple different tools and methods for analysis, and when historians are working on this for hours at a time, the work can become tedious, frustrating, and sometime unproductive. This leads to spending more time looking at a screen and figuring out how to use certain methods and tools, rather than focusing attention on the physical archive itself.

Creating a digital artifact from archival documents gives way to so many advantages. First of all, the majority of archival documents are in rough condition, and are very fragile to the touch. If digital artifacts were not a thing, most of what we know about history from these archival documents would be unknown. Some documents are illegible to the human eye but with technology, historians are able to recreate a lot of these archival documents.
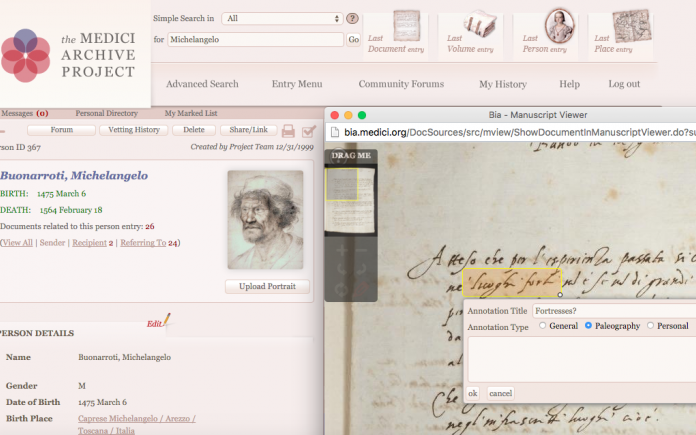
I think it is true that our physical and emotional relationships to our objects of study are shifting as we move deeper into a digital age. I think they are getting stronger and more intelligent, because a lot of the content that is being created connects directly to our natural human instincts, and can be very beneficial for people. As Whitley says in his paper, “Humans are quite adept at perceptual visual cues and recognizing subtle shape differences…humans are pre-wired for understanding and visualizing shape.” Because of this natural ability that humans possess, these digital tools that transform textual patterns into visual shapes naturally help people grasp certain skills of shape perception. There is even speculation that because this portion of the mind is being activated by these digital tools, it could potentially be accelerating the reading process.
Whitley talks about creating these things called “concept shapes” out of texts, to graphically represent data patterns. In order to better understand the content of a document, a group of scholars came up with a method for representing texts as “semi-spherical objects in a virtually rendered three dimensional space.” Wherever there are patterns in the text, the spherical objects “blend together to create a variety of quasi-organic shapes.” This method is one that seeks to help readers identify different patterns that would otherwise be overlooked if it was in a large body of text. For this, I believe it is true to say that digital versions of material texts highlight physical elements of texts that might otherwise pass unremarked.
One way to create online reading interfaces that can more closely approximate the experience of reading physical materials, that Whitley talks about in his paper is TextArc. It is an experiment in spatial reading, and is based off of the idea that seeing and reading are two complimentary processes. Whitley describes it basically as a “balancing act between reading and seeing.” As people are experiencing the text visualization, the eyes and the mind “scan for ideas, then follow the ideas down to where and how they appear in the text”.
Caleb Broughton is an Econ major who plays on the baseball team at Bucknell University. Born in Lebanon, NH on November 6, 1998.